What is OEE and how do I calculate the OEE ratio?
Manufacturing productivity is an important consideration for any company. Optimal manufacturing productivity can open up many opportunities for a company. One way to measure this manufacturing productivity is the tool OEE. How this tool can be used, how it optimizes production, increases productivity as well as improves cost usage, we will show in this article. In addition, you will find a practical example at the end of the article.

1. Key Areas
What is OEE? OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) is a measure of manufacturing productivity and describes overall equipment effectiveness. By measuring OEE, manufacturers are able to identify their strengths, understand their losses, evaluate their progress and ultimately improve the manufacturing process.
OEE measures effectiveness across the three key areas of availability, performance and quality.
1.1 Availability
Availability is the ratio of effective run time to pre-planned production time of the plant. To determine your effective runtime, take your planned production time and subtract all the time your manufacturing process is not running. In other words, the time that was due to both planned and unplanned stops. Examples of stops are changeovers, such as reconfiguring a machine, and breakdowns.
A score of 100% availability is only possible if the process runs uninterrupted during scheduled production.
1.2 Performance
Power is the ratio of net run time to maximum possible run time and takes into account anything that prevents the manufacturing process from running at the maximum possible power and speed. Slower process cycles and small downtime events reduce the overall performance.
A performance of 100 % is only possible if the process runs as fast as possible and without interruptions.
1.3 Quality
Quality is the ratio of good parts to the total number of parts produced. Good parts are all parts that successfully pass through the production process the first time without rework.
A score of 100% in quality is only possible if every part that passes through the production process is completely free of defects.
2. How do I calculate an OEE ratio?
Putting all three factors together gives the OEE value. Simply multiply all three ratios together: Availability times Performance times Quality equals OEE.

The calculation of an OEE ratio should provide the answers to two important questions:
– Am I using the equipment in production in an effective way?
– Where do measures need to be taken to improve the effectiveness of a piece of equipment?
3. Losses
As far as the effectiveness of a plant is concerned, a machine is unproductive if losses occur in one of the six major loss areas:
- Downtime
- Set-up
- Machine stops
- Reduced speed
- Scrap, rework, yield
- Start-up losses
These six loss areas are also reflected in the three categories or ratios “availability”, “performance” and “quality”.
3.1 Availability losses
Downtime losses are unplanned stoppages that require repair.
Changeover and adjustment losses occur during changeover or switching between products or production processes.
3.2 Power losses
Unscheduled stops and idling are often defined as a failure that lasts less than 10 minutes.
Reduced speed occurs when the machine runs at a lower speed than the planned design speed.
3.3 Quality losses
Defects lead to scrap or rework and are the consequences of a problem that has caused the machine to operate outside the predefined specification limits.
4. OEE evaluation
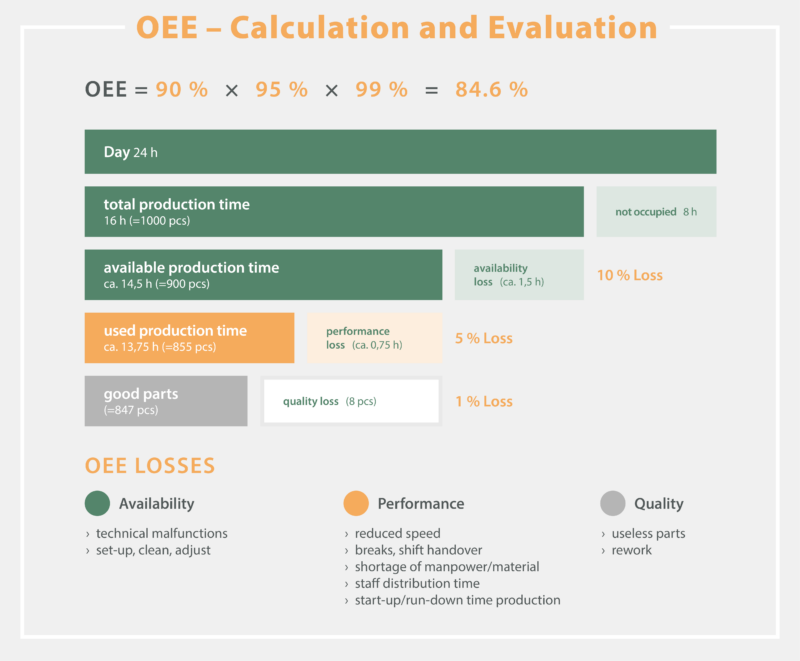
The final OEE assessment takes into account all losses that occur during the manufacturing process. This leads to an indicative value that shows the truly productive manufacturing time. For example, scores of 90 %, 95 % and 99 % in availability, performance and quality respectively can be multiplied together to give an OEE score of 84.6 %. Manufacturers can use the individual scores and the total score to identify where exactly operations can be improved.
In our example, increasing availability from 90% to 95% would improve OEE by almost five percentage points (95% x 95% x 99% = 89.3%). Even if an increase in availability to 95% would mean a reduction in quality by four points, i.e. the new quality ratio is only 95% instead of 99%, the overall process and OEE rating still improves (95% x 95% x 95% = 85.7%).
5. Planning
How do I plan an OEE determination in my production?
- Plan carefully on which machines you want to perform the OEE calculation. Are some of the machines a bottleneck? Are some of the machines overproductive?
- Involve the operators of the machines and form a cross-functional team.
- Collect robust data and involve their employees in the data collection.
- Evaluate the collected data and discuss it with your staff and teams.
- Put in place measures to improve your OEE and track your results in the continuous monitoring process.
Remember: OEE calculation is not the goal. The OEE calculation is a way to understand where the productivity of a machine is limited. It can also show which areas of production need to be addressed to increase productivity.
6. Summary
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a tool that can be used to increase the productivity of a plant.
Deciding when and where to improve productivity, by how much and at what cost, depends on each company’s individual goals and capabilities. To learn more about how you can monitor and improve your production processes, contact our experts and feel free to test our middleware OPC Router.
The OEE in Practice
Increasing the productivity of a facility is the focus of many companies. The OEE provides an overview of where productivity can be increased and to what extent. The approach is systematic. Commencing with the available production time, the total time during which production can be carried out in a plant or with a machine is first determined. For example, a machine can operate for 20 hours a day. However, due to various technical malfunctions and the associated repair work, the machine runs for only 16 hours. Therefore, there is a loss of 20%. Since this machine requires maintenance in several shifts, the daily loss due to the changeover time is 48 minutes and consequently another 5%. During this period, the company will produce 250 units, of which 5 units will have to be sorted out due to various production errors. So, 2% of the produced number of units are lost every day. The OEE calculation therefore looks as follows:
OEE = 80% x 95% x 98% = 74,48%
The company’s task is to improve the OEE score to 74.48%. The high failure during production time stands out in this context. By Using the software, such as the OPC Router, breakdowns can be noticed and fixed faster. Different services can notify the mechanic quicker to stop production, indicate a failure, and assist in repair. That would already greatly benefit the production in this example. Reducing downtime from two hours to one hour would increase the OEE score to 83.79%, almost an increase of 10%.
Further information
Machine data acquisition is the be-all and end-all when it comes to digitization in industry. Networked machines create a completely new transparency and thus better production control. This allows optimization opportunities in production processes to be uncovered. The most important basics and how the OPC router contributes to digitalization in manufacturing and production are explained in our article on machine data acquisition.
With the REST Plug-in, the OPC router is able to query and also address REST web services. Almost every system can be connected via the REST API and it is therefore possible to retrieve data from these systems and also to transfer data. REST functions can also be called via a REST trigger. This enables a separate REST API structure for various systems that are connected with other available Plug-ins.
A Telegram bot is an ideal way to transmit information from almost every imaginable area whenever you need it. We refer to this special bot function of the messenger in the article of the Knowledge Base “Technology” and also give simple instructions on how you can create a Telegram bot yourself.
Using our OPC Router Network File Access Plug-in, a network-wide file transfer and file handling can be realised. This Plug-in supports the FTP (File Transfer Protocol) as well as the SMB (Server Message Block) protocol. Via FTP, files can be exchanged between file servers in different networks if the corresponding FTP server service is provided.
Further interesting articles on the topics of Industry 4.0, cloud, technology, alerting and practical application examples as well as case studies can be found in our Knowledge Base.